|
|
|
| Reduction | Loss Oxygen |
| Gain Hydrogen | |
| Gain Electron | |
| Oxidation | Gain Oxygen |
| Loss Hydrogen | |
| Loss Electron |
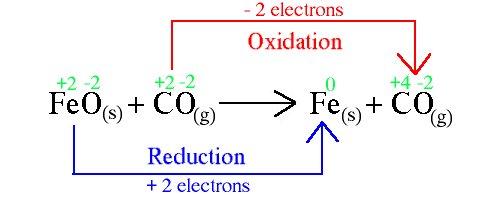
Following reaction is an example of redox reaction
The small green numbers written on the top are oxidation state
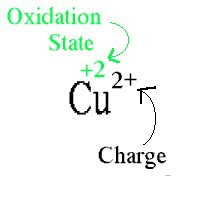
Oxidation state is " a measure of the number of electron an atom has gained or lost control of ".
e.g. CH3COOH (Acid) + H2O (Base) « CH3COO- (Base) +H3O+ (Acid)
Note: Acids partially dissociate in water are weak acids. A good example is ethanoic acid (CH3CH2OOH)
H2O+H2O «
H3O+ + OH-
(H3O+ = H+)
So it can be written as H2O «
H3O+ + OH-, let's express this in equilibrium equation.
Kc = [H+][OH-]/[H2O] rearrange this to
Kc[H2O] = [H+][OH-] call Kc[H2O] as a new constant Kw
Kw = [H+][OH-]
Experimentally the constant of water had been found and is 1.0 x 10-14 mol2dm-6 at 25oC.
Thus Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14 mol2dm-6 at 25oC
Since water is neautral (i.e. amount of acid = amount of base)
[H+] = [OH-]
[H+][OH-] = 1.0x10-14
X2 = 1.0x10-14
X = 1.0x10-7
Thus [H+] = 1.0 x 10-7
So the concentration of acid in water is 1.0 x 10-7
As we have calculated earlier, the concentration of acid in water is 1.0 x 10-7 so if we put this into the PH equation
pH = -log [1.0 x 10-7]
pH = 7
The table below shows how much H+ is present in each pH.
| Acid | |||||||
| pH | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Concentration of H+ | 1 x 100 | 1 x 10-1 | 1 x 10-2 | 1 x 10-3 | 1 x 10-4 | 1 x 10-5 | 1 x 10-6 |
Note: when calculating pH of an Alkaline, simply substitute the concentration of OH- with H+ (i.e. pH = -log[OH-])and subscribe by 14.
For instance 0.1 mole of NaOH will be
pH = -log[0.1]
pH = 1.0
14-1=13
Thus, pH for 0.1 mole of NaOH is 13.
Here is the table for Alkaline
| Base | |||||||
| pH | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 |
| Concentration of OH- | 1 x 100 | 1 x 10-1 | 1 x 10-2 | 1 x 10-3 | 1 x 10-4 | 1 x 10-5 | 1 x 10-6 |
| Contents & give your comment | Structure and Bonding | Inorganic Chemistry | Organic Chemistry | Physical Chemistry | Calculation | Techniques | Definitions | Periodic table | References |